The Implications for Remote Physiological Monitoring and Remote Therapeutic Monitoring Reimbursement in Private and Public Insurance in the United States

Increased utilization of RPM and RTM codes could signal a promising future for remote healthcare and digital therapeutics.
The ripple effects of 2020 will be felt for quite some time. Over two years of medical, political, and social upheaval changed many things, but maybe none more profound to the healthcare industry than the widespread adoption of telehealth and services. It took months of social distancing, mask wearing, and quarantining to make patients realize just how valuable a virtual doctor’s visit could be. But, now, thanks to a growing body of evidence of its effectiveness and new legislation that could pave the way for reimbursement parity for providers delivering virtual care, telehealth appears to be here to stay.
This, of course, raises the question: As telehealth becomes an increasingly prevalent form of care delivery, how will that evolution affect health outcomes and influence the journeys of patients throughout the healthcare system?
Some signs that the mainstreaming of telehealth is having a positive impact on patient engagement can be seen in the adoption of Remote Physiological Monitoring (RPM) and Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM) systems, whereby providers use telehealth to monitor patient medication adherence and review physiological data that is automatically transmitted via wearables and other electronic devices.
Until recently, it was impossible to track how these technologies were being used. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) only introduced reimbursement codes for RPM in January of 2018 and the billing codes for RTM were just introduced in January of 2022. The creation of these codes has made it possible not only for clinicians to get reimbursed for remote monitoring, but also to better understand the impacts of that monitoring on patient outcomes.
As part of our collective work to support the expansion of digital health and telemedicine, Komodo Health and the Digital Therapeutic Alliance have teamed up to publish a landscape analysis using RPM and RTM codes to identify important trends in care. This paper examined the volume of patients served, what types of providers are utilizing the codes, which therapy areas are benefiting from use, and how COVID-19 has affected overall adoption.
In our analysis of 330 million unique patient journeys, we found that both RPM and RTM code utilization has seen a steady increase, and — while overall telemedicine usage has plateaued following the pandemic — RPM and RTM code utilization continued to demonstrate considerable growth.
For example, we found that, over the last four years, there have been over 50,000 unique healthcare providers located at over 19,000 healthcare organizations that have billed for an RPM code. Of these providers, 64% began using the codes during the pandemic (starting March 2020).
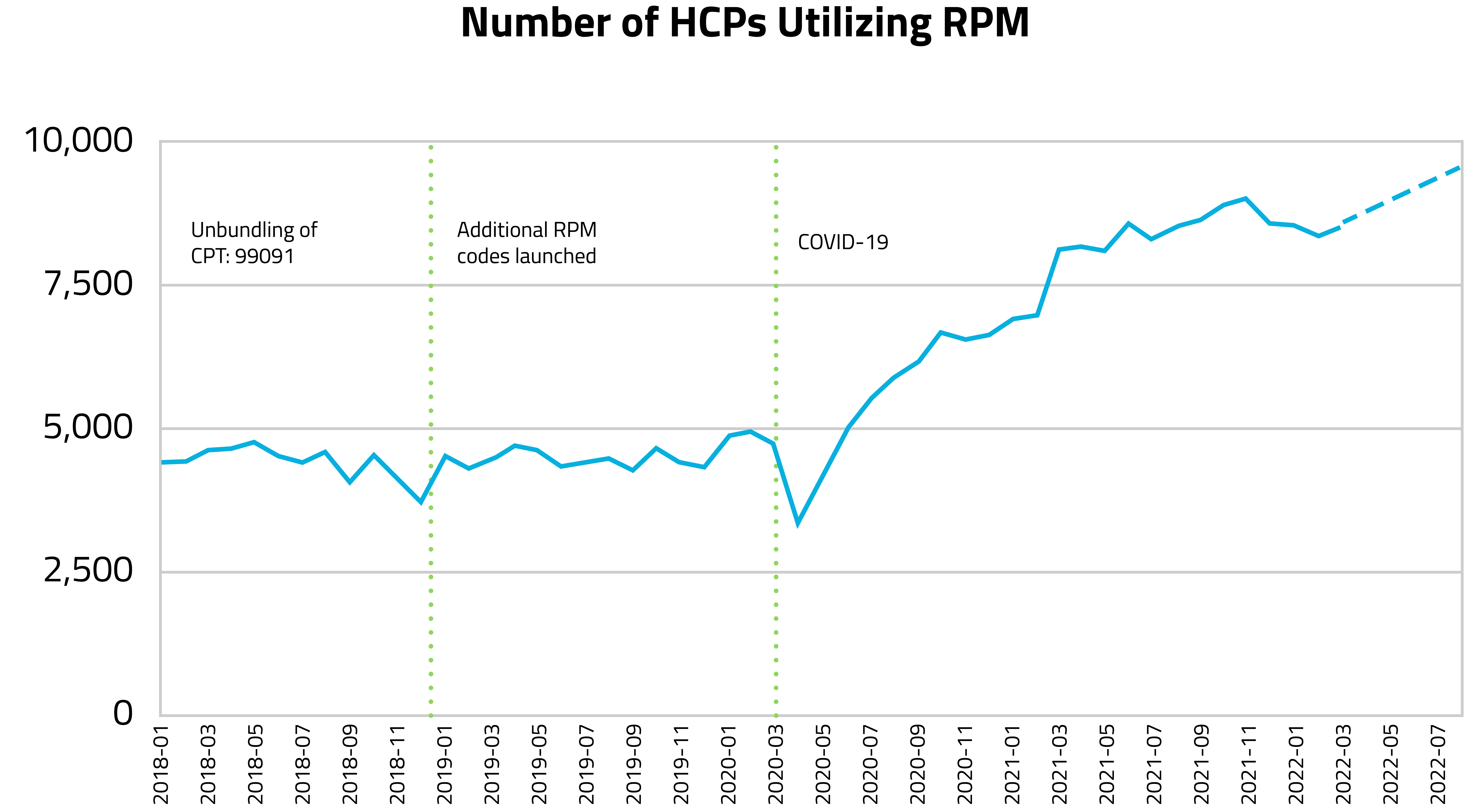 Prior to the onset of COVID-19, use of RPM codes had been stable but, predictably, the pandemic caused a significant surge in usage, leading to the number of providers using the codes per month to nearly double. The analysis also found a steady increase in the utilization of RTM codes since their January 2022 launch. Although the data is limited, given the recency of the codes, over 500 providers had utilized RTM codes by May 2022.
Prior to the onset of COVID-19, use of RPM codes had been stable but, predictably, the pandemic caused a significant surge in usage, leading to the number of providers using the codes per month to nearly double. The analysis also found a steady increase in the utilization of RTM codes since their January 2022 launch. Although the data is limited, given the recency of the codes, over 500 providers had utilized RTM codes by May 2022.
Only by tracking these trends in RPM and RTM adoption — as well as overall telehealth utilization at the macro level — is it possible to truly understand the impact these technologies are having on the individual healthcare experiences of patients and their providers. This initial analysis demonstrates some positive trends in early adoption of the technology, but it will be important to keep studying not only how often RPM and RTM are used, but also to identify trends in where they are being used most, what types of patients and providers are seeing the greatest levels of RPM and RTM engagement, and how these remote touchpoints are affecting outcomes. Future analyses in this series will dig deeper into these trends using Komodo’s Prism and Sentinel solutions to spotlight the key points in the patient journey where telehealth is having the greatest impact.
Paper authors: Alona May, Director of Solution Design, Komodo Health, Di Jiang, Area Vice President, Med Tech and Digital Therapeutics, Komodo Health, Andy Molnar, CEO, Digital Therapeutics Alliance, Lani Hessen, Vice President of Patient Access, Digital Therapeutics Alliance, and Dr. Steven Driver, Medical Director of DTx at Advocate Aurora Health and Interventional Cardiologist








